
Sharma Industries - Jodhpur, Rajasthan (India)
Proud to be associated with

Planted 10,000 saplings in Haryana, India
Year: 2019
An initiative by:

In 2019, a total of 42 farmers from 12 villages of Haryana have been shortlisted for planted 10,000 saplings of multiple species after an in-depth assessment of their farms undertaken by the Earthworm team.
1. After an in-depth farm assessment, interested farmers were shortlisted. 2. As per the agroforestry experts' suggestions, relevant species for the Haryana region were selected. 3. Quality saplings were procured from nurseries and transported to the farms.
Meeting with farmers to sensitize them about the importance of trees and encourage them for plantation.

Suitable space at farms was identified to plant saplings. The existing status of soil,ground water, and biodiversity at the farms were recorded.

A panel of agroforestry experts has been constituted to seek recommendations on suitable species for Haryana region.
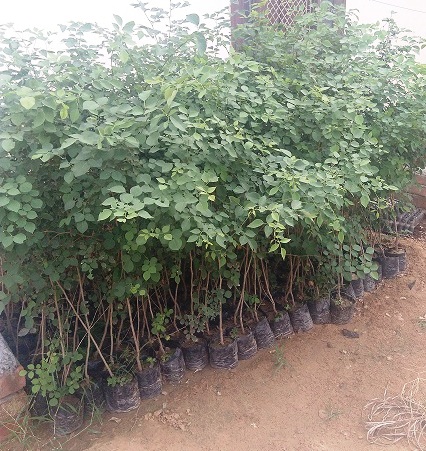

Quality saplings have been developed at nurseries under the supervision of the Earthworm team.
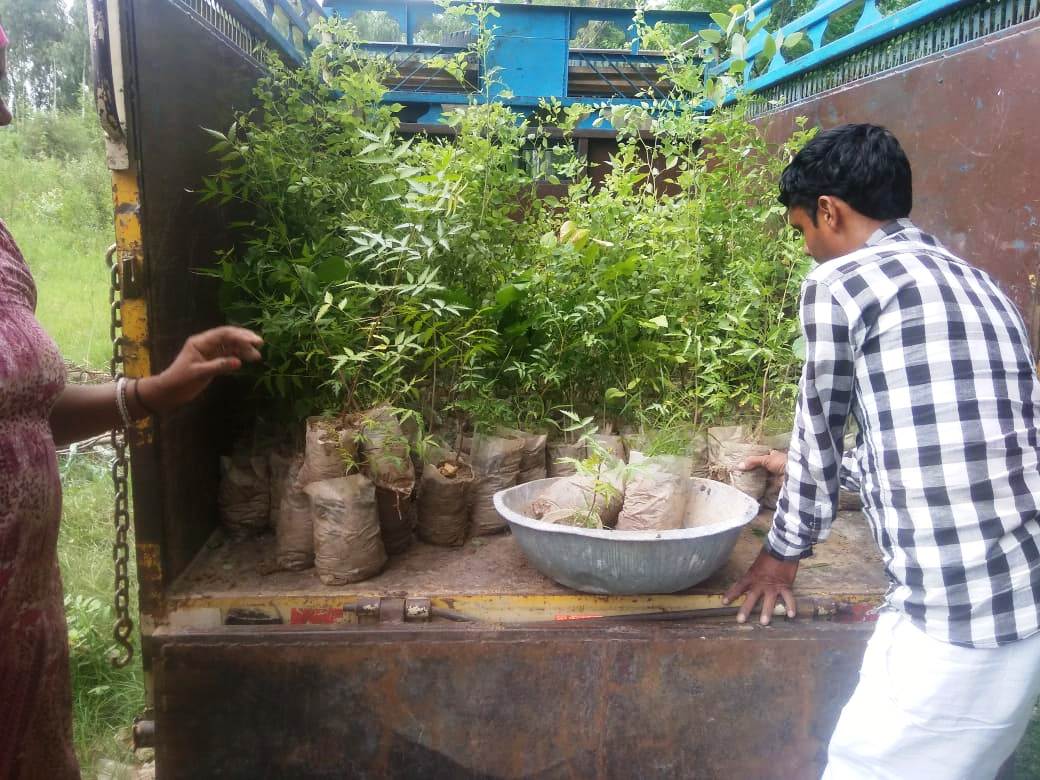

Saplings are properly transported and special attention was given during loading and unloading of saplings.
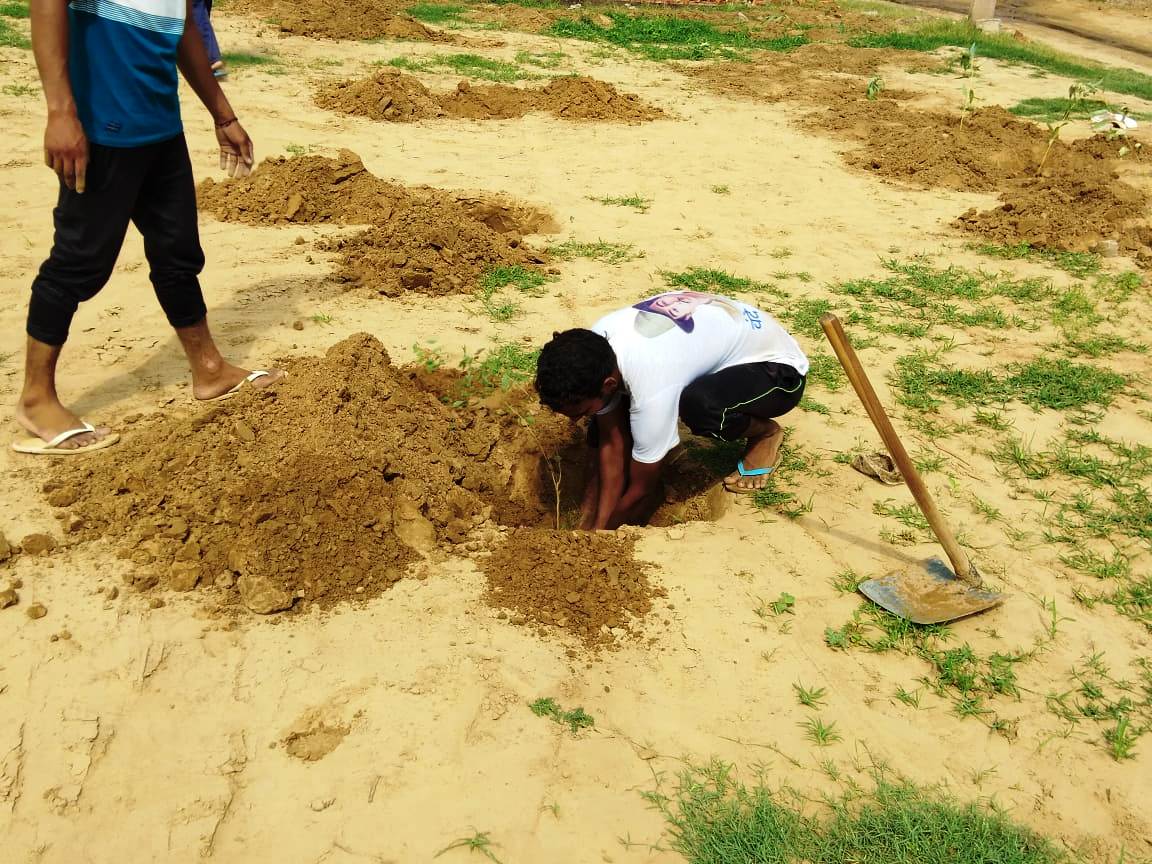

Saplings are planted at farms following the recommended planting techniques.
To enhance the soil health and biodiversity, the following species consisting of timber, fruit and flower has been planted at different farms.
| Sr. No. | Scientific Name | Local Name | Saplings Planted |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dalbergia sissoo |
Shisham | 6627 |
| 2 | Syzygium cumini |
Jamun | 1215 |
| 3 | Phyllanthus emblica |
Amla | 610 |
| 4 | Melia species |
Bakain | 595 |
| 5 | Azadirachta indica |
Neem | 503 |
| 6 | Terminalia arjuna |
Arjun | 450 |
| Total Saplings Planted | |||
The campaign aims to record tree growth measured in terms of height and girth. It will be updated every quarter.
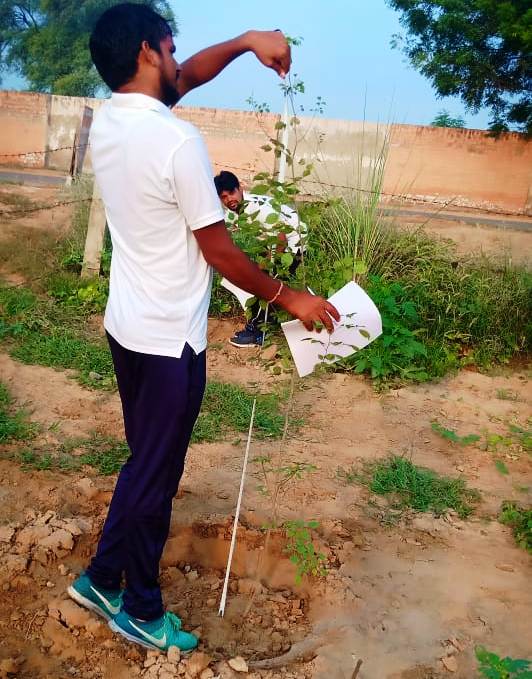

The height and girth of each sapling were measured. These parameters varied inter and intra-specific hence average height and girth has been calculated based on each species.
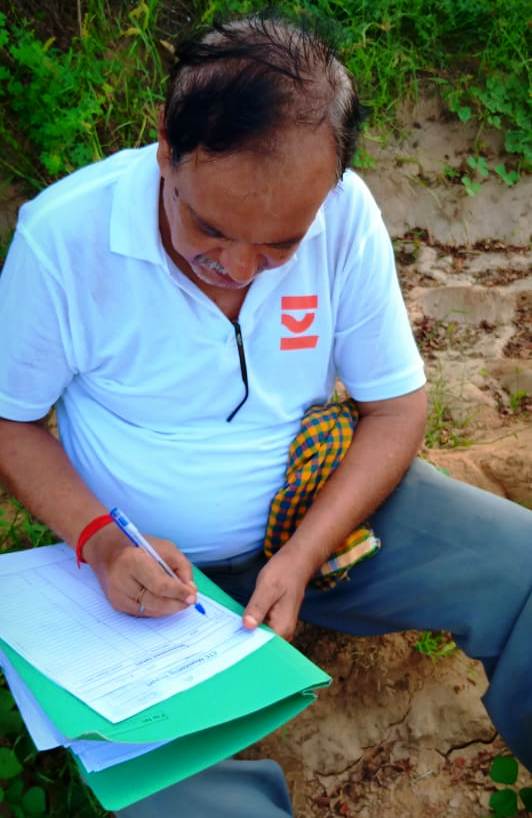

The data thus measured resulted in the quantitative measurement of impact like biomass, carbon stock, and carbon dioxide sequestrated.
| Sr. No. | Species (Local Name) |
Baseline Data | Quarterly Update | Growth % | Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) |
Girth (cm) |
Height (cm) |
Girth (cm) |
Height (%) |
Girth (%) |
|||
| 1 | Sheesham | 85.51 | 0.50 | 142.12 | 6.88 | 66.20 | 1275.88 | - |
| 2 | Jamun | 64.75 | 0.41 | 129.04 | 6.64 | 99.28 | 1504.89 | - |
| 3 | Amla | 47.24 | 0.19 | 102 | 6.62 | 115.99 | 3406.46 | - |
| 4 | Bakain | 58.98 | 0.25 | 133.10 | 6.86 | 125.66 | 2647.83 | - |
| 5 | Neem | 55.50 | 0.34 | 123.40 | 6.73 | 122.33 | 1781.59 | - |
| 6 | Arjun | 69.92 | 0.44 | 132.13 | 6.63 | 88.98 | 1400.14 | |
This data is till June' 2022
Every single tree has got many impacts on human life and environment and with 10,000 saplings on the ground, significant positive influences are expected. Below is the report of key impact parameters and activities.

Regular plantation of appropriate trees species helps reduce soil erosion from bare land
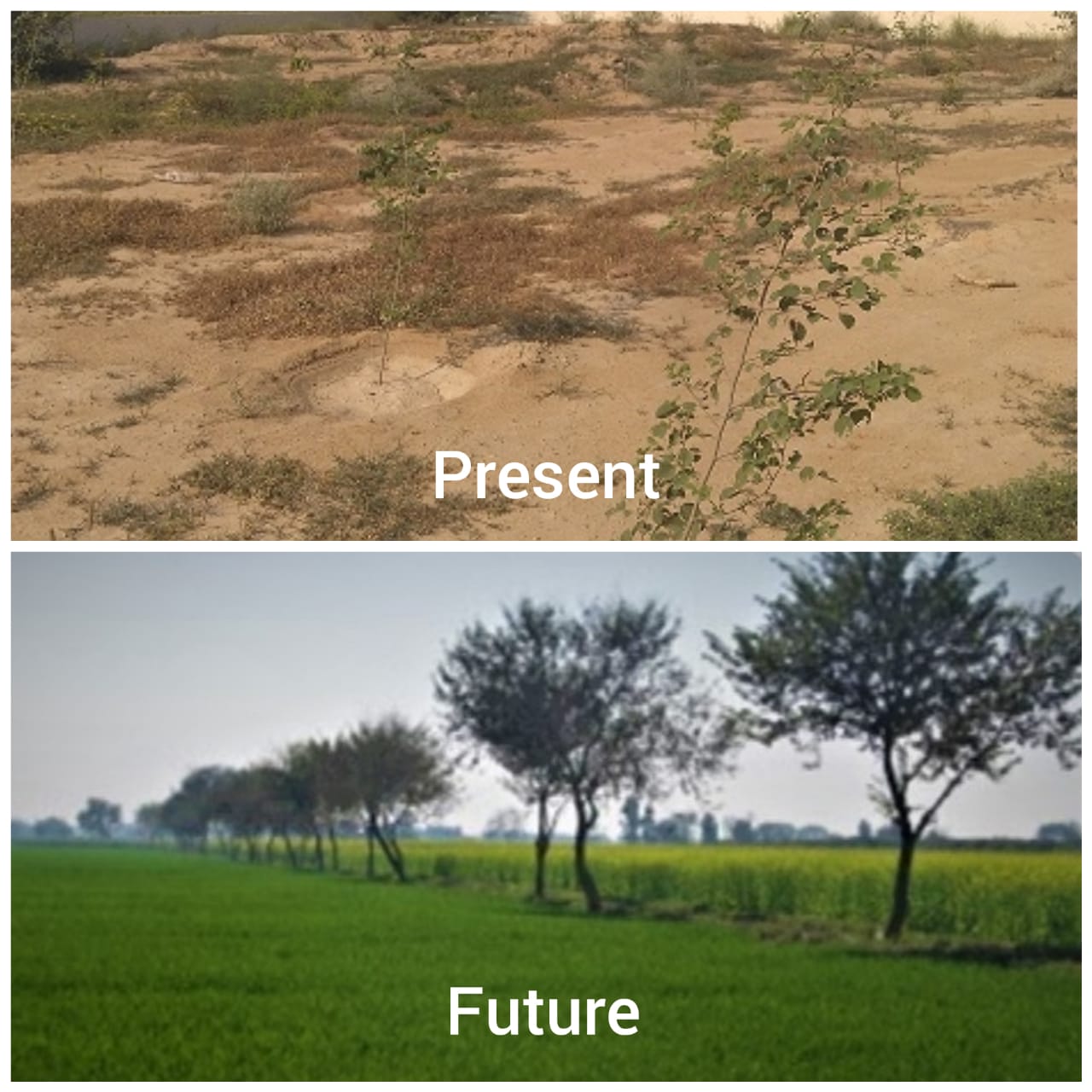

Plantation of tree species increases the green cover of the area and improves biodiversity at farms.
| Sr. No. | Parameters | Details | Remarks | Future Projection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Farmers typology | Farmers shortlisted for this lot are of different categories. 35% are small/ marginal, 30% are medium and 35% are large. The main focus has been given to small and medium-scale farmers to improve their resilience. | Farmer's typology is generally developed based on their landholding is to categorize them among marginal to large scale categories. | With the agroforestry model, small and marginal farmers will become more resilient when these trees will get mature and make them open for new experiments such as chemical-free farming. |
| 2 | Land area covered | A total of 535 acres of land has been covered under this plantation. Majority of saplings are planted on the boundary of farms. | Saplings planted on farms will prevent soil erosion and increase soil moisture and improve soil fertility. | Projection about impact will be made after a couple of quarters of monitoring. |
| 3 | Survival rate of saplings | The current survival rate is 69%. | The average survival of different species of saplings is in the range of 50- 60%. | It is assumed that the survival percentage of saplings may be at 60- 70%.. |
| 4 | Canopy cover | Average canopy cover of the species under CTC may range between 4-10 meters in diameter. | Canopy cover of a tree can be defined as the proportion of area covered by the vertical projection of tree crowns. | The canopy cover in the next 10 years of the plantation may cover 19- 116 Acres which is in between 4- 24% of total land area covered. |
| 5 | Above-Ground Biomass | The current above-ground biomass is around 2877 kg. | Above-ground biomass is the most visible of all the carbon pools, and changes in it are an important indicator of change or of the impact of an intervention on benefits related to both carbon mitigation and other matters. Above-ground biomass is a key pool for most land-based projects. | It is predicted that the above-ground biomass will be around 762- 882 tons. |
| 6 | Below-Ground Biomass | The current below-ground biomass is around 748 kg. | The root system is important not only for anchoring trees in the soil but it also fulfils a variety of physiological functions such as water and nutrient absorption from the soil and storage of carbohydrates. Tree roots significantly contribute to the total biomass and carbon storage in forests. | It is predicted that the below-ground biomass will be around 198- 231 tons. |
| 7 | Total Biomass | The current total biomass is around 3626 kg. | Biomass is a measure of biological matter, expressed in weight. Total of above and below-ground biomass. | It is predicted that the total biomass will be around 960- 1120 tons. |
| 8 | Carbon stock | The current carbon stock is around 1813 kg. | Carbon stock is the amount of carbon that has been sequestered from the atmosphere and is now stored within the forest ecosystem. | It is predicted that the carbon stock will be around 480- 560 tons. |
| 9 | Carbon dioxide sequestered | Total carbon dioxide sequestered is around 6641 kg. | Through the biochemical process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is taken in by trees and stored as carbon in the trunk, branches, leaves, and roots. Carbon is also stored in the soil and indeed this is a major sink for carbon in the forest. | It is predicted that carbon dioxide sequestration will be around 1758- 2051 tons. |
| 10 | Soil pH | Based on the observations made during farm assessment, soil pH has been found between 7.7 to 7.9. | Soil pH is very important because it directly affects soil nutrient availability. Plant roots can only absorb nutrients after they have been transformed into certain ionic forms. | Soil pH is very important because it directly affects soil nutrient availability. Plant roots can only absorb nutrients after they have been transformed into certain ionic forms. |
| 11 | Soil quality | Based on soil testing, the soil is loamy sand with low low organic carbon around 0.41%. | Soil quality is the capacity of a specific kind of soil to function, within natural or managed ecosystem boundaries, to sustain plant and animal productivity, maintain or enhance water and air quality, and support human health and habitation. | Over a period of time, trees improve the soil's structure and improve its fertility and help in preventing soil erosion. Probing root growth breaks up the soil, which creates spaces for storing air and water. Tree roots improve drainage because each root acts as an underground water channel to help water penetrate the soil. |
We collaborate with partners in many different ways, from receiving donor funds to developing tools, techniques, and projects.
Recently, media has covered the program run by Earthworm in Punjab region to address the concerns related to soil health, biodiversity, cancer disease caused by excessive use of chemicals in farming and others.
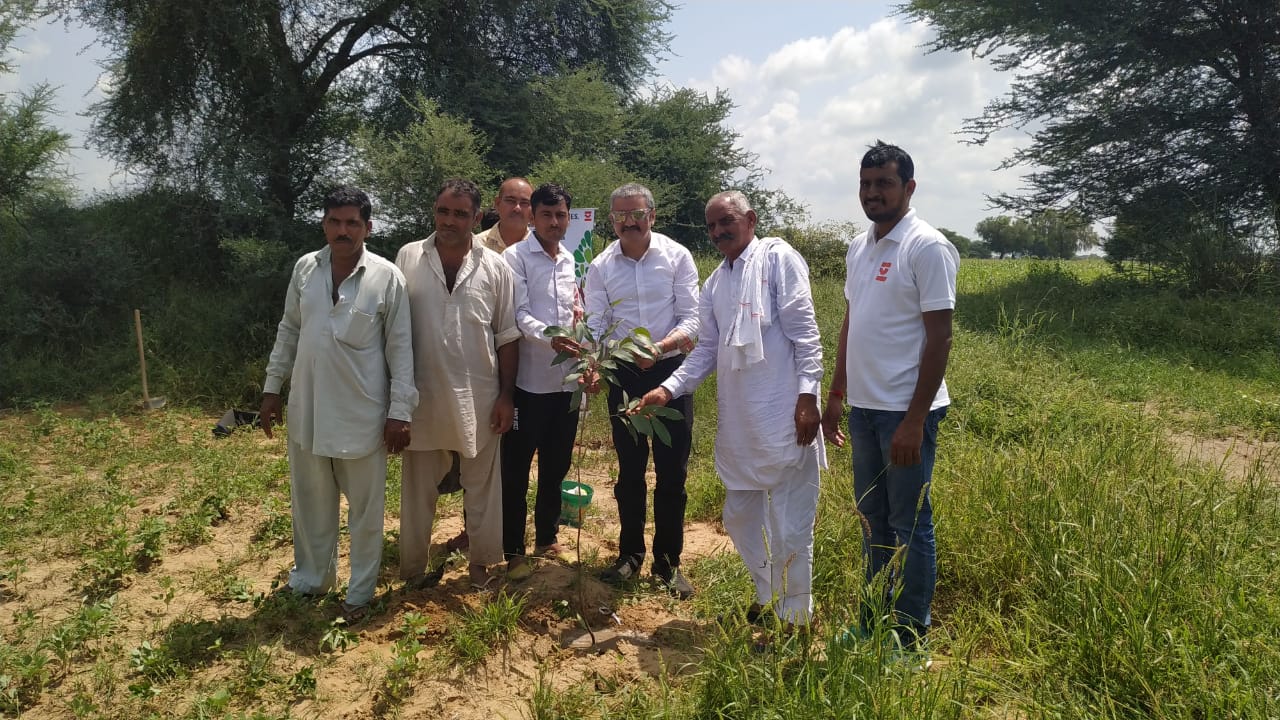

Mr. Praveen Sharma along with his family from Sharma Industries participated in the plantation.
Earthworm Foundation is a non-profit organisation built on values and driven by the desire to positively impact the relationship between people and nature. With most of our staff operating directly on the ground where the issues are, we work with our members and partners to make value chains an engine of prosperity for communities and ecosystems. In fact, we see a world where forests are a boundless source of materials and a home for biodiversity; communities see their rights respected and have opportunities to develop; workers are seen as productive partners, and agriculture becomes the instrument to feed a hungry planet and keep our climate stable.

We envision a global society that respects itself and the needs of nature. To achieve our vision, we partner with businesses and other with the same goal of solving the social and environmental challenges our world faces, working in a pragmatic way from boardrooms to farms, boots on the ground. We know we can’t tackle deeply-rooted challenges alone. We collaborate with partners in many different ways, from receiving donor funds to developing tools and projects together.